Understanding the difference between UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) design is crucial for creating effective digital products. While UX focuses on enhancing user satisfaction through usability and overall experience, UI emphasizes the visual and interactive elements that make a product appealing and easy to navigate.
In this article, we’ll break down these key differences and explore how they work together to create seamless user experiences. Whether you’re a designer or a business owner, grasping these concepts is essential for building successful applications and websites. Let’s get started!
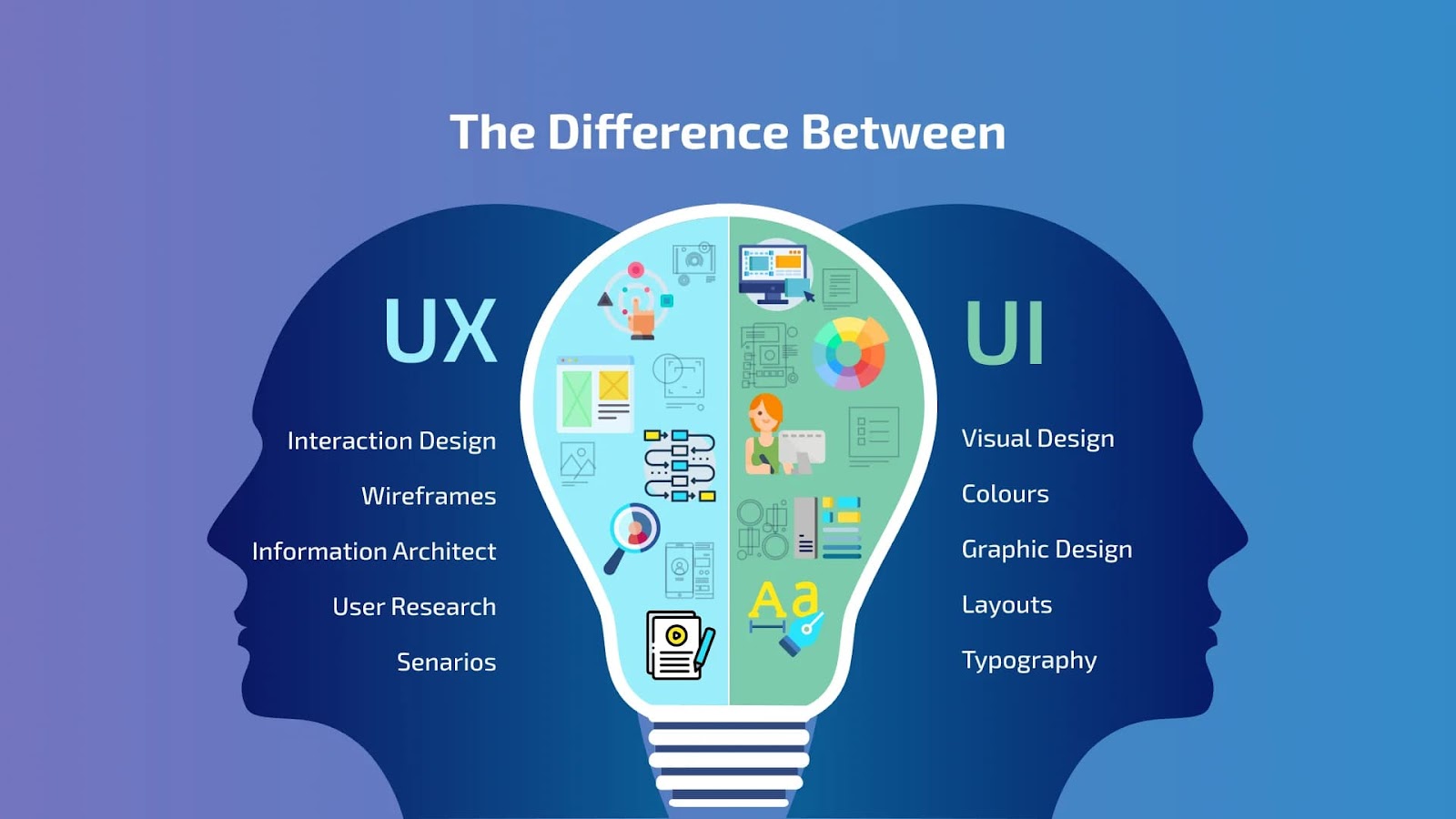
Difference between UI and UX
The difference between UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) design is fundamental yet often misunderstood. Here’s a brief overview of each:
User Interface (UI) Design
UI design refers to the visual elements and interactive components of a digital product. This includes layout, colors, typography, buttons, icons, and overall aesthetics. The goal of UI design is to create an attractive interface that guides users seamlessly through the product, making it intuitive and enjoyable to use.
User Experience (UX) Design
UX design encompasses the overall experience a user has while interacting with a product. It involves researching and understanding user needs, behaviors, and pain points to create a product that is not only usable but also valuable and satisfying. UX design focuses on the entire journey a user takes, from the initial encounter to the final interaction, ensuring that every touchpoint is optimized for a positive experience.

Key Differences
- Focus: UI is about the look and feel of the product, while UX is about the overall experience.
- Components: UI design includes visual elements; UX design involves user research, testing, and information architecture.
- Goal: UI aims to enhance the visual appeal and interactivity, whereas UX seeks to improve usability and user satisfaction.
Roles and Responsibilities: What UX and UI Designers Do
Understanding the tasks and responsibilities of UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) designers is essential for grasping how they contribute to creating effective digital products. While their roles are distinct, they often collaborate closely to ensure a cohesive user experience.
UX Designer Responsibilities
1. User Research: UX designers conduct qualitative and quantitative research to understand user needs, behaviors, and pain points. This may involve surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
2. Information Architecture: They create a structured framework for the content within the product, ensuring users can navigate intuitively. This includes site maps and user flows.
3. Wireframing and Prototyping: UX designers develop wireframes and prototypes to visualize the user journey, allowing for testing and iteration before final implementation.
4. User Testing: Conducting usability tests helps identify issues and gather feedback, which is essential for refining the design and improving the user experience.
5. Collaboration: UX designers work with stakeholders, developers, and UI designers to ensure that the user’s perspective is integrated throughout the product development process.
UI Designer Responsibilities
1. Visual Design: UI designers focus on creating the look and feel of the product. This involves selecting color palettes, typography, and imagery to create an appealing aesthetic.
2. Interactive Elements: They design interactive components such as buttons, sliders, and menus, ensuring that these elements are user-friendly and enhance the overall experience.
3. Style Guides and Design Systems: UI designers develop style guides and design systems that maintain consistency across the product, providing a cohesive look and feel.
4. Responsive Design: Ensuring that the interface is adaptable to various devices and screen sizes is a critical aspect of UI design, enhancing accessibility for all users.
5. Collaboration: UI designers collaborate closely with UX designers to align the visual elements with the user experience, making adjustments based on user feedback and testing.
Tools for UX and UI Design
To effectively handle UX and UI design, designers rely on specialized tools that streamline each aspect of the process, from research and wireframing to prototyping and visual design. Here are some key tools that are widely used by both UX and UI designers:
UX Design Tools
1. User Research:
- Google Analytics: Provides insights into user behavior, helping UX designers understand user needs and pain points.
- Hotjar: Records user interactions, showing where users click and scroll, which can identify usability issues and areas for improvement.
- SurveyMonkey or Typeform: Enables designers to gather feedback and insights directly from users through surveys.
2. Wireframing and Prototyping:
- Figma: A popular tool that allows designers to create and collaborate on wireframes, prototypes, and interactive elements.
- Sketch: Known for its flexibility in wireframing and prototyping, particularly popular among Mac users.
- Adobe XD: Offers a comprehensive suite for wireframing, prototyping, and user testing, making it suitable for end-to-end UX design.
3. User Testing:
- Maze: Integrates with Figma and Adobe XD, allowing designers to test prototypes and gather feedback quickly.
- UsabilityHub Provides tools for testing designs and gathering user insights, helping to validate design choices early on.
UI Design Tools
1. Visual Design:
- Adobe Illustrator: Great for creating icons, illustrations, and custom graphic elements.
- Photoshop: Useful for image editing, creating high-fidelity visuals, and handling complex UI elements.
- Canva (for simpler needs): Useful for creating UI assets quickly, especially if full graphic design software isn’t necessary.
2. Prototyping and Animation:
- InVision: Enables designers to create interactive mockups, link screens, and add animations to showcase the flow of the product.
- Principle: Ideal for creating more complex animations and transitions that mimic real user interactions.
- Framer: Provides advanced animation capabilities, allowing UI designers to create highly interactive interfaces.
3. Design Systems:
- Zeplin: Helps designers collaborate with developers by providing design specs, assets, and style guides in a format that developers can easily understand.
- Storybook: Often used by UI teams to create, document, and test UI components, ensuring consistency across a product.
Conclusion: Why Both UX and UI Designers Are Essential
Having both UX and UI designers on a team is critical to building a successful digital product. UX designers ensure that a product meets user needs by focusing on the entire journey—from ease of navigation to overall satisfaction. They dive into research, structure information, and design intuitive paths to make sure users can interact with the product effortlessly. Meanwhile, UI designers bring these journeys to life visually, creating an appealing and cohesive interface that is not only functional but also engaging.
By combining their skills, UX and UI designers create products that are both user-centered and visually striking, balancing functionality with aesthetics. While UX ensures that the product is valuable and solves user problems effectively, UI makes sure it looks and feels inviting. Together, they provide a seamless experience that drives engagement, improves satisfaction, and boosts brand loyalty.
For companies looking to deliver competitive and user-friendly digital solutions, having both UX and UI designers is invaluable. With our team at NetForemost, you can leverage expert UX and UI design to create high-impact applications. Ready to elevate your project? Schedule a call with us to discuss how we can bring your vision to life.






